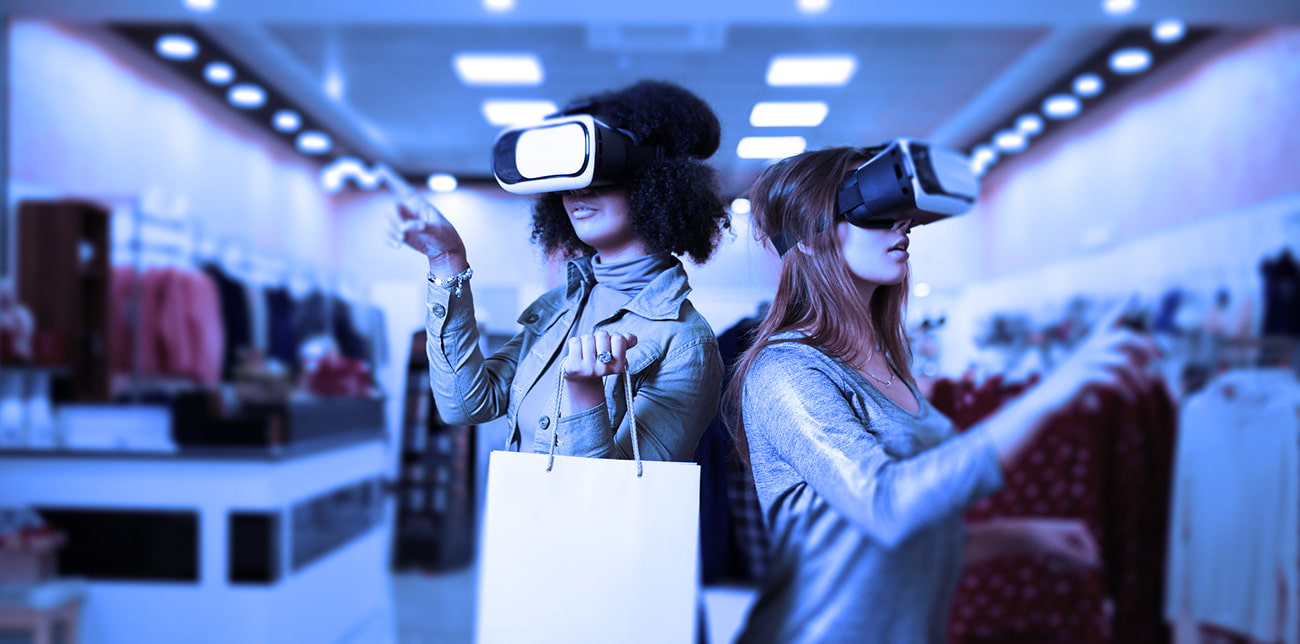
With the uptick in digital shopping, retailers have gotten creative in offering a full-service experience to customers. Many have achieved this by integrating extended reality into in-person and online shopping platforms. extended reality offers retailers a method to replicate popular facets of the in-person experience to online shoppers, and it helps make the in-person shopping experience more immersive. By adopting these tools, retailers can enhance customer service while keeping up with the competition.
Table of Contents
- > The extended reality definition: What XR means
- > Benefits of using extended reality in customer engagement
- > Challenges and limitations of extended reality
- > Extended Reality vs. VR vs. AR vs. MR
- > How extended reality could evolve the retail shopping experience
- > Best practices for implementing extended reality in retail
- > The future of extended reality in retail
- > Key trends and statistics about extended reality
- > Embracing the future of retail with extended reality
The extended reality definition: What XR means
Extended reality (XR) collectively refers to augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR). This technology marries elements of the physical world and the digital world, allowing people to interact online similarly to how they would in person. Yet, knowing “how does extended reality work?” is complex.
Extended reality creates an immersive experience by creating a digital world that mirrors reality. This industry is expected to be worth over $120 billion by 2026. This technology has the power to transform people’s lives, allowing them to see popular tourist spots without leaving their living rooms, for instance. Retailers can also use it to create an unparalleled user experience for customers across the globe.
Benefits of using extended reality in customer engagement
XR technology offers multiple benefits to retailers since they can use it to create unique experiences for their customers. According to research, customer experience is a top priority for many businesses. It’s one of the best ways to stand out, and extended reality is a great way to implement and create these memorable customer interactions. Extended reality also offers:
- Immersive experiences
- Enhances product visualization
- Personalized and customized experiences
- Increased convenience and accessibility
- Improved connectivity with customers
- Improved warehouse management
Benefit #1: Immersive experiences
With extended reality technology, retailers can replicate and improve the in-person experience for virtual shoppers. Using extended reality glasses and other tools, online shoppers can interact with merchandise and better understand how they can use it.
For example, a clothing retailer can use augmented reality to create virtual change rooms that give online shoppers the option to try on clothing to see its fit and color.
Benefit #2: Enhances product visualization
Extended reality development is not just for clothing. Retailers of all types can use these tools to help customers visualize merchandise in their own lives. A furniture store can add augmented reality to its app, allowing customers to snap a pic of their room and digitally add and arrange pieces of furniture.
Retailers can also set up virtual product demonstrations in the Metaverse and other virtual reality settings, walking customers through the features of their merchandise.
Benefit #3: Personalized and customized experiences

More than half of customers say they will shop again with businesses offering a personalized experience. Retailers can use extended reality to replicate an on-location, personalized concierge service. Using virtual or mixed reality, the store can guide the customer through inventory that would interest them, customizing recommendations based on the shopper’s preferences and past purchases.
For example, if someone is shopping for wall art for their home, he can explore specific genres and browse through inventory that suits his taste. He can also use augmented reality to check how the piece of art would look in each room.
Benefit #4: Increased convenience and accessibility
The days when people were limited by geographical boundaries are gone. High-end retailers such as Saks Fifth Avenue or Bergdorf Goodman only opened stores in locations with specific demographic criteria. With extended reality, customers who can afford to patronize these shops can access them without traveling to a large city.
Customers with mobility issues are no longer limited by inaccessible storefronts. With XR, they can shop from home in an environment that lets them interact with the merchandise, trying it on and seeing it in action through product demos.
Benefit #5: Increased connectivity with customers
With extended reality, brands can create tailored campaigns and push them out through the metaverse and other digital channels. These campaigns can connect with a customer’s emotions while giving them the ability to visualize each product.
Virtual reality and augmented reality give customers a new and exciting way to engage with a brand. For example, while playing a virtual reality video game, a customer may see an ad for a new car and schedule a virtual test drive.
Benefit #6: Improved warehouse management
Because AR technology integrates with inventory systems and offers multiple ways to efficiently collect data, retailers can use it to monitor their inventory. The technology retailers use to automate warehouse management and distribution can connect with XR systems, so customers never see out of stock products during their virtual experience.
Challenges and limitations of extended reality
While extended reality offers a host of benefits to retailers, it’s still an emerging landscape that presents challenges. Extended reality development is ongoing, meaning companies work hard to improve the experience. However, a retailer may face the following limitations:
- Cost and implementation
- User adoption and accessibility
- Content creation and integration
- Limited physical interaction
- Customer security risks
Challenge #1: Cost and implementation
Extended reality implementation requires detailed hardware, software, and infrastructure, leading to high execution and investment costs. A customized app offering a robust selection of augmented reality features can take as much as nine months to develop and may cost up to $300,000.
Smaller retailers looking to compete with established brands may not have the capital to implement an app with all the needed features. They may need to research extended reality jobs and add positions to keep their virtual showrooms current.
Challenge #2: User adoption and accessibility

Extended reality only works when customers take advantage of it. These technologies are still in their infancy and have yet to be adopted on a large scale. By 2027, AR and VR are estimated to surpass 100 million users. Compared to over 7 billion global mobile phone users, this number is not impressive.
With such a low adoption rate, customers may not feel comfortable with the technology or they may not be familiar with it. Additionally, XR experiences may cause some to experience motion sickness or other discomfort. Plus, the tech may not work correctly for people with disabilities, limiting their ability to engage.
Challenge #3: Content creation and integration
Retailers still need to create content for their extended reality platforms, particularly when they want to personalize experiences. This usually requires working with a developer who turns the retailer’s vision into an extended reality.
To be successful, an extended reality environment should include engaging environments, 3D models, and interactive elements. These programs also need to be integrated into existing retail systems and workflows, including inventory management and checkout processes, for example. Creating content for extended reality takes time and a specialized skill set that could deter retailers from using it.
Challenge #4: Limited physical interaction

Although extended reality opens up retailers to customers around the world, there are limitations to how people can interact with merchandise. Customers can try on simulated clothing, but they can’t feel the fabric or touch the fasteners. Plus, a customer shopping for furniture in the virtual environment can’t sit on a sofa to determine its comfort level.
Challenge #5: Potential compromise of customer security
Extended reality requires an internet connection, making it hard to protect customer data. Augmented reality technology sees what a user is doing, which might turn some customers off to the experience. As extended reality best practices and applications evolve and improve, there may be better ways to safeguard customer data. However, in its current state, customers may shy away from the technology.
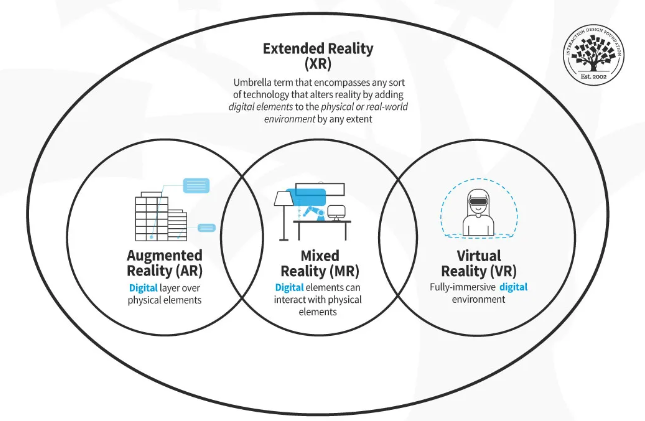
Extended Reality vs. VR vs. AR vs. MR
Extended reality, virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality are all related technologies that offer varying levels of immersion. Let’s explore them in detail to build an understanding of their similarities and differences.
1. Extended reality vs. virtual reality
- Definition: Extended reality is an umbrella term covering all immersive technology, including virtual reality. Virtual reality is a simulated experience that uses special equipment to create the feeling of the real world. It isolates the user into a completely simulated environment.
- Immersion Level: Extended reality can include full immersion or limited immersion. Virtual reality refers to a fully immersive digital environment.
- Interaction: Customers using virtual reality need access to headsets, controllers, and other haptic devices that control their motion and interaction with their virtual world.
- Use Cases: Virtual reality is popular in gaming, virtual tours, training simulations, and entertainment that offers a truly immersive experience.
2. Extended reality vs. augmented reality
- Definition: Extended reality covers augmented reality and other technology. Augmented reality is an immersive technology that imposes computer-generated imagery onto a user’s view of reality.
- Immersion Level: Augmented reality is only partially immersive since only parts of the user’s experience are digital.
- Interaction: Customers can access many augmented reality technologies on their smartphones. Retailers already offer this tool for virtual jewelry fittings, makeup trials, and more.
- Use Cases: Augmented reality is popular in gaming, such as the Pokémon GO concept that swept the country in the mid-2010s. It is also one of many extended reality solutions to surgical science, allowing surgeons to access patient records and scans without taking their hands off the patient.
3. Extended reality vs. mixed reality
- Definition: Extended reality covers mixed reality. Mixed reality offers users a combination real-world environment and one that is computer generated.
- Immersion Level: Mixed reality is more immersive than AR but less so than VR.
- Interaction: To interact in a mixed reality environment, customers need the right types of computer equipment, including processors that allow for 360-degree interaction. They also need a headset, a controller, and other equipment that controls haptics.
- Use Cases: Mixed reality allows users to watch sports matches in a way that feels as though they are in the arena. It’s also popular in research, development, and construction, allowing developers and builders to test designs without wasting materials.

How extended reality could evolve the retail shopping experience
There are many potential ways to engage customers and enhance their experience using extended reality.
1. Engaging virtual retail journeys
Extended reality best practices allow a retailer to replicate the best parts of the in-person shopping experience. Brands, including Charlotte Tilbury and Nike, allow customers to shop in a virtual store, try on merchandise, and join live events.
These experiences take customers beyond what they would get shopping on a smartphone, allowing them to see and sample merchandise and learn more about products. By giving users the chance to see how products look on them, these brands can guide a customer toward a purchase.
2. Reducing return rates
Because extended reality offers better product visualization than a simple online catalog, customers are less likely to return their items. Companies that offer augmented reality services such as virtual try-on had a 22 percent lower return rate.
Shoppers buying clothing and cosmetics online are limited to the models featured on the site. It’s hard to see how different cuts work on various body shapes. Something they think looks flattering on a model may accentuate parts of their body that make them self-conscious, causing them to return the item. With AR, they can see how a piece of clothing would realistically look on them, and if they don’t like it, they won’t buy it.
3. Immersive in-store shopping experiences
Extended reality is not limited to online shopping. Retailers can also use it to improve the in-store experience. Some furniture retailers allow customers in the store to scan a QR code and use the app to visualize how a piece would look in their home. With extended reality technology, customers can receive personalized recommendations, view inventory levels of items they want to buy, and watch product tutorials all while in the store.
4. AR shopping assistant
Augmented reality enhances the in-store experience by eliminating the need for multiple sales assistants on the floor. When sales associates are assisting other customers, people can use AR to access product information. AR shopping assistants can also guide customers to in-store deals and give them access to product catalogs. They can also offer personalized product recommendations.
5. Virtual product customization
Using virtual product customization, a retailer can create 3D visualizations of their products. When a customer accesses their virtual store, these visualizations allow customers to interact with the product, similar to how they would in person. Customers can also use these tools to create specialized products that are made-to-order. This might include a bespoke suit, swag with a company’s logo, or engraved jewelry.
6. Virtual showrooms and virtual fitting
Virtual showrooms allow brands to connect with users online in a more immersive environment. Customers get a 360-degree view of merchandise and they can engage with it more than they could on a traditional platform.
They can also upload their measurements into the system to virtually try on merchandise. With big-ticket items such as wedding dresses or expensive suits, a virtual fitting saves a customer time while also helping them envision the product. Virtual fittings are also great for people who don’t like the traditional fitting room experience with harsh lighting and multiple mirrors.
Best practices for implementing extended reality in retail
These companies lead the way in extended reality, improving the unique customer experience.
How Accenture utilizes extended reality for creating customer experiences
Accenture is an extended reality group developing solutions that offer XR experiences. Extended reality Accenture solutions include everything from immersive learning to virtual merchandising. The company has helped multiple retailers create virtual showrooms that provide an experience that rivals in-store shopping.
The company has also worked with retailers to broaden their circle for market research, gathering insights from people on a larger scale to help retailers improve products and service delivery. This company is full of extended reality experts who know best practices and help retailers create the best XR platform for their brands.
How BMW deploys XR in self-driving simulations
BMW recently created a mixed-reality simulator to offer immersive driving experiences to the masses. The company’s M2 vehicle serves as the controller in the mixed-reality simulation. Users operate the car wearing a headset that immerses them in a virtual world controlled by the car they’re driving in the real one.
As an example of extreme reality, this unique system allows users to drive in places they’ve never considered while they’re actually on a closed course. If this seems unsafe, the car monitors real-world conditions, and the simulator keeps users on the actual road.
How IKEA gives customers flexibility
IKEA was one of the first companies to experiment with XR, launching an augmented reality feature in 2013 that would allow customers to visualize furniture in their rooms. This has become a key part of the shopping experience in the past decade, saving customers from setting up a piece of furniture only to find that it doesn’t fit into their room.
The future of extended reality in retail
Although extended reality hasn’t completely permeated the retail landscape yet, many companies are jumping on board. Retailers are currently using it to improve brand awareness and maintain an edge over the competition.
In the future of retail, brands may use XR with AI for a more unique, personalized experience. AI-powered tools can learn from each user’s interactions with the site to tailor their experience. With multiple retailers jumping on chatbots and other AI-based tools, this partnership is a natural progression of the omnichannel experience.
Key trends and statistics about extended reality
As the extended reality for business grows and evolves, pay attention to these trends and statistics. Extended reality numbers are increasing as technology improves. Here’s how.
Interesting extended reality stats
- XR innovation is most robust in the Asia-Pacific region and the United States. (Thrive My Way)
- XR is expected to be worth about $300 billion globally by 2024. (Thrive My Way)
- 42% of customers would be more willing to adopt XR if the devices were smaller and more fashionable. (Thrive My Way)
- 2 in 5 customers stated they would pay more for a product they could test with AR. (Exploding Topics)
The newest extended reality trends in retail
- Retailers can start leveraging AR to get new customers. (Proven Reality)
- Retailers can use the extended reality metaverse to connect with potential customers in the real world. (XR Today)
- As technology improves, retailers can use it to appeal to more senses in the virtual world. (XR Today)
Embracing the future of retail with extended reality
Extended reality opens retailers up to once inaccessible customers. By creating an extended reality stage, a virtual showroom, and virtual assistants, retailers can create immersive experiences to connect with customers and enhance their shopping experience.
By giving customers a better way to visualize and try out merchandise, retailers can potentially make more sales with fewer returns. They can also build brand awareness and establish themselves as retail leaders.
With more people adopting AR, VR, and MR in their daily lives, retailers who skip this trend risk missing out on tech-savvy customers. Yet, you don’t have to grow your business alone. ContactPigeon’s growth experts can help any eCommerce brand scale, mainly as retail trends grow and evolve. Keep up with the competition. Schedule a free consultation today.

Let’s Help You Scale Up
Spending time on Linkedin? Follow us and get notified of our thought-leadership content:





